Retargeting with PyRoki¶
This workflow covers retargeting SMPL humanoid motions from AMASS to robot morphologies (G1 and H1_2) using PyRoki, a trajectory optimization-based retargeting tool.
How Retargeting Works¶
Unlike many common retargeters that solve inverse kinematics (IK) frame-by-frame, PyRoki performs trajectory-level kinematic optimization. This means:
Whole-trajectory optimization: Instead of solving each frame independently, PyRoki optimizes the entire motion trajectory at once. This makes it much easier to maintain temporal consistency and smoothness.
No sudden flips: With our modified PyRoki implementation, we almost never see failures of sudden motion flips and discontinuities. This is critical for large-scale data processing and training.
Multiple cost terms: The optimization balances several objectives simultaneously:
Local alignment (
local_alignment): Matches relative joint/keypoint positions and bone directions between source and targetGlobal alignment (
global_alignment): Matches absolute keypoint positions to robot link positions in world frameRoot smoothness (
root_smoothness): Penalizes jittery root motionJoint smoothness (
joint_smoothness): Penalizes jittery joint motionJoint limits (
limit_cost): Keeps joints within valid rangesJoint velocity limits (
joint_vel_limit): Prevents unrealistic joint speedsFoot contact (
foot_contact): When feet are in contact, penalizes foot movement and maintains ankle-toe height consistencyFoot tilt (
foot_tilt): Keeps feet flat when in contact
Fixed trajectory length: All motions are trimmed or padded to 15 seconds (450 frames at 30 FPS) for efficient JAX compilation and batch processing.
Overview¶
The full retargeting pipeline from AMASS to robot:
Packaged AMASS MotionLib (.pt, SMPL format)
│
▼ (extract_retargeting_input_keypoints_from_packaged_motionlib.py)
Keypoints (.npy files)
│
├──────────────────────────────────────┐
▼ ▼
Retargeted robot motion Contact labels from source
(batch_retarget_to_<robot>_from_keypoints.py) (--save-contacts-only)
│ │
└──────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼ (convert_pyroki_retargeted_robot_motions_to_proto.py)
ProtoMotions format (.motion)
│
▼ (motion_lib.py)
Packaged MotionLib (.pt)
Prerequisites¶
Packaged AMASS MotionLib in SMPL format (see AMASS Data Preparation)
PyRoki installed in a separate Python environment (see below)
Installing PyRoki¶
PyRoki requires a separate Python environment from ProtoMotions due to different JAX/CUDA dependencies. Install it as follows:
# Create a new environment for PyRoki
conda create -n pyroki python=3.10
conda activate pyroki
# Clone and install PyRoki
git clone https://github.com/chungmin99/pyroki.git
cd pyroki
pip install -e .
For more details, see the PyRoki GitHub repository.
Quick Start: Convenience Script¶
For a one-click solution, use the provided bash script. Since ProtoMotions and PyRoki require separate Python environments, you must provide paths to both Python interpreters:
./scripts/retarget_amass_to_robot.sh <proto_python> <pyroki_python> <amass_pt_file> <output_dir> <robot_type> [skip_freq]
Arguments:
proto_python: Path to Python interpreter with ProtoMotions installedpyroki_python: Path to Python interpreter with PyRoki installedamass_pt_file: Path to packaged AMASS MotionLib .pt fileoutput_dir: Directory for all outputsrobot_type: Target robot (g1orh1_2)skip_freq: (Optional) Skip every N motions (default: 1 = all motions)
Example:
# Retarget every 50th motion to G1 (for quick testing)
./scripts/retarget_amass_to_robot.sh \
~/miniconda3/envs/protomotions/bin/python \
~/miniconda3/envs/pyroki/bin/python \
/path/to/amass_train.pt \
/path/to/output \
g1 50
# Retarget all motions to H1_2
./scripts/retarget_amass_to_robot.sh \
~/miniconda3/envs/protomotions/bin/python \
~/miniconda3/envs/pyroki/bin/python \
/path/to/amass_train.pt \
/path/to/output \
h1_2 1
The script runs all steps automatically and outputs the final MotionLib .pt file.
Step-by-Step Guide¶
Step 1: Extract Keypoints from Packaged MotionLib¶
Extract simplified keypoints (pelvis, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, ankles, feet, plus auxiliary points) from the packaged SMPL motions:
python data/scripts/extract_retargeting_input_keypoints_from_packaged_motionlib.py \
/path/to/amass_train.pt \
--output-path /path/to/keypoints/ \
--skeleton-format smpl \
--start-idx 0 \
--skip-freq 15
Arguments:
--output-path: Directory for extracted keypoint.npyfiles--skeleton-format: Source skeleton format (smplfor AMASS)--start-idx: Starting motion index (default: 0)--skip-freq: Skip every N motions (use 15-35 for quick subset testing, 1 for all motions)
Tip
Use --skip-freq 50 or higher when first testing the pipeline to process
only a small subset of motions. Once verified, set --skip-freq 1 to
process all motions.
Step 2: Run PyRoki Retargeting¶
Activate the PyRoki environment (separate from ProtoMotions) and run batch retargeting:
For G1:
conda activate pyroki # Switch to PyRoki environment
python pyroki/batch_retarget_to_g1_from_keypoints.py \
--keypoints-folder-path /path/to/keypoints/ \
--output-dir /path/to/retargeted_g1/ \
--source-type smpl \
--subsample-factor 1 \
--no-visualize \
--skip-existing
For H1_2:
python pyroki/batch_retarget_to_h1_2_from_keypoints.py \
--keypoints-folder-path /path/to/keypoints/ \
--output-dir /path/to/retargeted_h1_2/ \
--source-type smpl \
--subsample-factor 1 \
--no-visualize \
--skip-existing
Arguments:
--keypoints-folder-path: Input directory with keypoint.npyfiles--output-dir: Output directory for retargeted motions (.npzfiles)--source-type: Source skeleton type (smplfor AMASS,rigv1for custom rigs)--subsample-factor: Temporal subsampling (1 = no subsampling)--no-visualize: Skip visualization (required for batch processing)--skip-existing: Resume interrupted runs by skipping completed files
Step 3: Extract Contact Labels from Source Motions¶
Foot contact labels should come from the source SMPL motions, not re-computed from retargeted robot motions. This is because the retargeting process can be imperfect, and source motion contacts are more reliable.
python pyroki/batch_retarget_to_g1_from_keypoints.py \
--keypoints-folder-path /path/to/keypoints/ \
--source-type smpl \
--subsample-factor 1 \
--save-contacts-only \
--contacts-dir /path/to/contacts/ \
--skip-existing
The --save-contacts-only flag skips retargeting and only extracts processed
foot contact labels from the source keypoints.
Step 4: Convert to ProtoMotions Format¶
Convert retargeted motions to ProtoMotions format, incorporating the source contact labels:
python data/scripts/convert_pyroki_retargeted_robot_motions_to_proto.py \
--retargeted-motion-dir /path/to/retargeted_g1/ \
--output-dir /path/to/retargeted_g1_proto/ \
--robot-type g1 \
--contact-labels-dir /path/to/contacts/ \
--apply-motion-filter \
--force-remake
Arguments:
--retargeted-motion-dir: Directory with retargeted.npzfiles--output-dir: Output directory for.motionfiles--robot-type: Target robot (g1orh1_2)--contact-labels-dir: Directory with contact labels from Step 3--apply-motion-filter: Apply smoothing filter to reduce jitter--force-remake: Overwrite existing files
Note
The conversion script automatically adjusts the robot height (fix_height) to
ensure feet don’t penetrate the ground, using robot-specific foot offsets.
Step 5: Package into MotionLib¶
Package the converted motions into a single .pt file:
python protomotions/components/motion_lib.py \
--motion-path /path/to/retargeted_g1_proto/ \
--output-file /path/to/retargeted_g1.pt
Step 6: Verify with Motion Visualizer¶
Before training, verify the retargeted motions look correct using the motion visualizer:
python examples/motion_libs_visualizer.py \
--motion_files /path/to/retargeted_g1.pt \
--robot g1 \
--simulator isaacgym
The visualizer supports comparing multiple MotionLibs side-by-side:
python examples/motion_libs_visualizer.py \
--motion_files /path/to/retargeted_g1.pt /path/to/reference.pt \
--robot g1 \
--simulator isaacgym
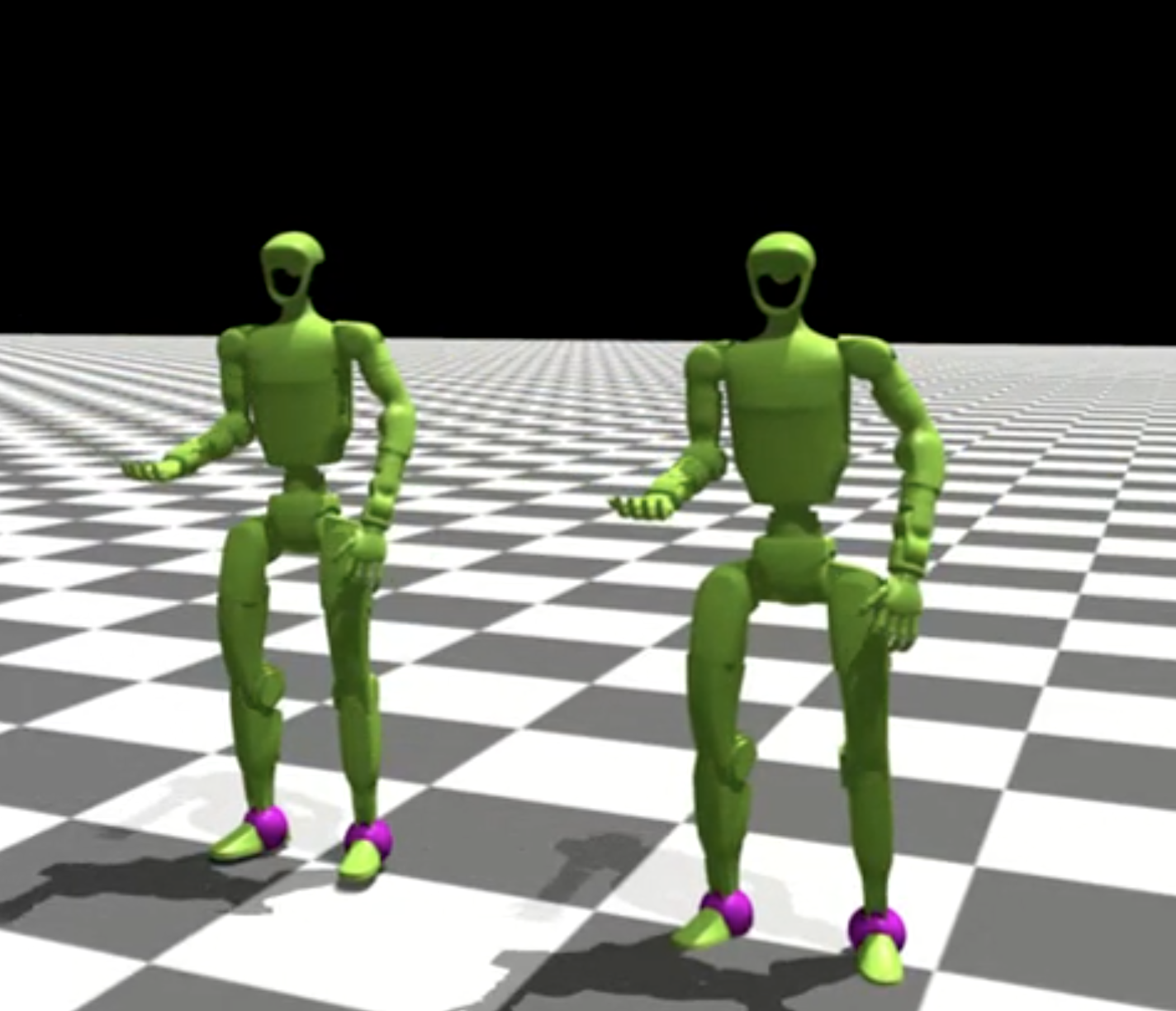
Controls:
R: Switch to next motion
1/2: Increase/decrease playback speed
3/4: Adjust smoothness threshold for highlighting
Adding a New Robot for Retargeting¶
To retarget to a new robot, create a new retargeting script based on existing ones.
Comparing batch_retarget_to_g1_from_keypoints.py and
batch_retarget_to_h1_2_from_keypoints.py shows the key differences:
Link Name Mapping
Update the keypoint-to-link mapping in
get_humanoid_retarget_indices():# G1 example for human_name, g1_name in [ ("pelvis", "pelvis_contour_link"), ("left_hip", "left_hip_pitch_link"), ("left_knee", "left_knee_link"), ("left_ankle", "left_ankle_roll_link"), ("left_foot", "left_foot_link"), ("left_shoulder", "left_shoulder_pitch_link"), ("left_elbow", "left_elbow_link"), ("left_wrist", "left_wrist_yaw_link"), # ... right side similarly ]: # H1_2 example for human_name, h1_2_name in [ ("pelvis", "pelvis"), ("left_hip", "left_hip_yaw_link"), ("left_knee", "left_knee_link"), ("left_ankle", "left_ankle_roll_link"), ("left_foot", "left_foot_link"), ("left_shoulder", "left_shoulder_roll_link"), ("left_elbow", "left_elbow_link"), ("left_wrist", "left_wrist_yaw_link"), # ... right side similarly ]:
Keypoint Scaling
Different robots have different proportions. Adjust the scaling factors in
load_motion_data()to match your robot’s size:# G1 (smaller robot) if source_type == "smpl": simplified_keypoints_lower_body_local = ( simplified_keypoints_lower_body_local * onp.array([0.9, 0.9, 0.85])[None, None, :] ) simplified_keypoints_upper_body_local = ( simplified_keypoints_upper_body_local * onp.array([0.9, 0.9, 0.8])[None, None, :] ) # H1_2 (larger robot, closer to human scale) if source_type == "smpl": simplified_keypoints_lower_body_local = ( simplified_keypoints_lower_body_local * onp.array([1.1, 1.1, 1.1])[None, None, :] ) simplified_keypoints_upper_body_local = ( simplified_keypoints_upper_body_local * onp.array([1.1, 1.1, 1.0])[None, None, :] )
Auxiliary Point Offsets
Update hand and torso auxiliary point offsets in
pc_alignment_cost():# G1 hand auxiliary point left_hand_aux_pos = link_pos_left_wrist + link_rot_mat_left_wrist @ jnp.array( [0.0, 0.0, 0.14] # G1 specific offset ) # H1_2 hand auxiliary point left_hand_aux_pos = link_pos_left_wrist + link_rot_mat_left_wrist @ jnp.array( [0.0, 0.0, 0.2] # H1_2 specific offset )
URDF and Mesh Paths
Update default paths for your robot’s URDF and mesh files:
parser.add_argument( "--urdf-path", default=str(SCRIPT_DIR / "../protomotions/data/assets/urdf/for_retargeting/your_robot.urdf"), ) parser.add_argument( "--mesh-dir", default=str(SCRIPT_DIR / "../protomotions/data/assets/mesh/YourRobot"), )
Optimization Weights
Tune the optimization weights for your robot:
weights_dict = RetargetingWeights( local_alignment=1.0, global_alignment=4.0, # G1: 4.0, H1_2: 3.0 root_smoothness=1.0, joint_smoothness=4.0, self_collision=0.0, joint_rest_penalty=1.0, joint_vel_limit=50.0, foot_contact=30.0, foot_tilt=1.0, )
Update Conversion Script
Add your robot type to
convert_pyroki_retargeted_robot_motions_to_proto.pyto handle robot-specific processing (joint ordering, height offsets, etc.).
Next Steps¶
AMASS Data Preparation - Prepare AMASS data
SMPL Training on AMASS - Train SMPL policy on AMASS
Adding a Custom Robot - Add your own robot to ProtoMotions